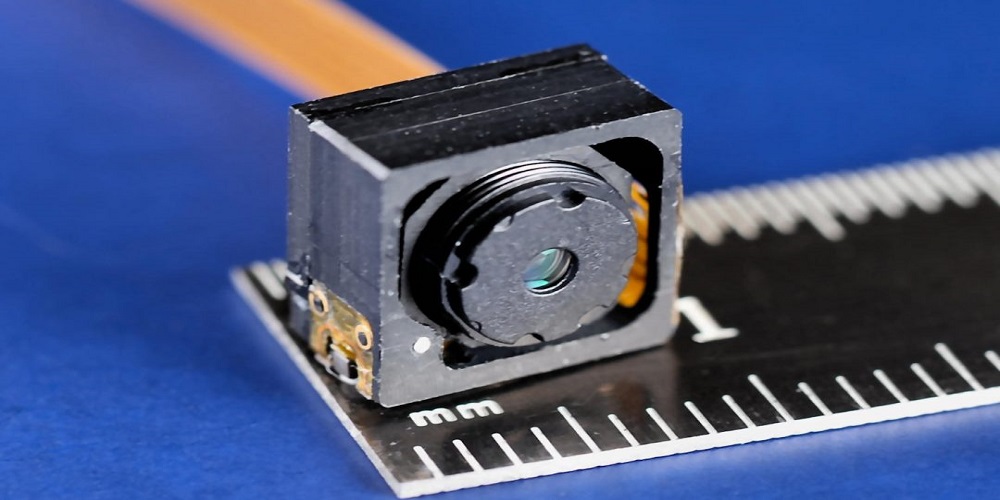
The ability to autofocus (AF) has completely changed how we take pictures in modern photography. Even in dim lighting or when the subject moves, we can quickly and precisely Auto Focus on our subjects. But a crucial element, the Voice Coil Motor, is required to achieve this precision (VCM).
What is Auto Focus?
The photographer had to turn a focusing ring on the lens to change the focus distance on older manual focus cameras. This procedure might be tiresome, especially when capturing moving objects or in dimly lit situations. Autofocus technology streamlines this process by using sensors built into the camera to detect contrast or phase differences in the subject and automatically adjust the focus distance.
Auto Focus uses two main techniques: phase detection and contrast detection.
- The camera’s image sensor is used to detect the contrast between the subject and the background in contrast detection, which is primarily used in mirrorless cameras.
- On the other hand, phase detection uses a specific AF sensor and a different mirror system to identify the phase difference between two points. DSLR cameras mostly use phase detection because it is quicker than contrast detection.
What is VCM?
The Voice Coil Motor (VCM) is an electric motor that transforms electrical energy into mechanical motion using a magnet and a coil. Moving the lens elements back and forth to change the focus distance is a common technique used in camera lenses. VCMs are perfect for contemporary camera systems because they are lightweight and small. They enable the camera to focus in a split second and are quick and precise.
How Do VCM and Auto Focus Work Together?
For achieving precise and quick focusing, modern cameras combine Auto Focus and VCM. The camera notifies the VCM to move the lens elements to the appropriate position when it detects the need for focus adjustment. Once the subject is in focus, the VCM moves the lens elements to change the focus distance.
One benefit of using VCM in Auto Focus systems is the ability to adjust the focus distance precisely. This precision can obtain sharp images even at large apertures with shallow depths of field. Additionally, because VCMs move quickly, the camera can track moving objects and change the focus distance in real-time.
Different Types of VCM
Linear VCM and Rotary VCM are the two main types of VCM used in camera lenses.
- The most typical VCMs used in camera lenses are linear VCMs. They have a straight path for the back-and-forth movement of the lens elements. For use in zoom and telephoto lenses, linear VCMs are ideal because they allow linear focus distance adjustment.
- As their name implies, rotary VCMs rotate the lens components to change the focus distance. Wide-angle and pancake lenses frequently employ them. Rotary VCMs are smaller and lighter than linear VCMs, making them ideal for compact camera systems.
Conclusion
The world of photography has revolutionized thanks to autofocus and VCM technology. They have made it simpler for photographers to quickly and accurately capture images, even in difficult lighting conditions. Modern cameras must have VCMs because they enable accurate and quick adjustments to the focus distance. We anticipate seeing even more advancements in Auto Focus and VCM technology as the technology develops, further enhancing our capacity to take beautiful pictures.